Design
project-based|
learning experiences.
Join thousands of educators & students using Inkwire's AI copilot to design and engage in experiential learning.








Schools, Districts, and Professional Learning Organizations
Scale your instructional vision,
accelerate professional learning
Give your educators & students Inkwire's AI-powered tools to activate your instructional frameworks within their day-to-day workflows.
Contact us to learn morePlan with an AI-assisted instructional framework
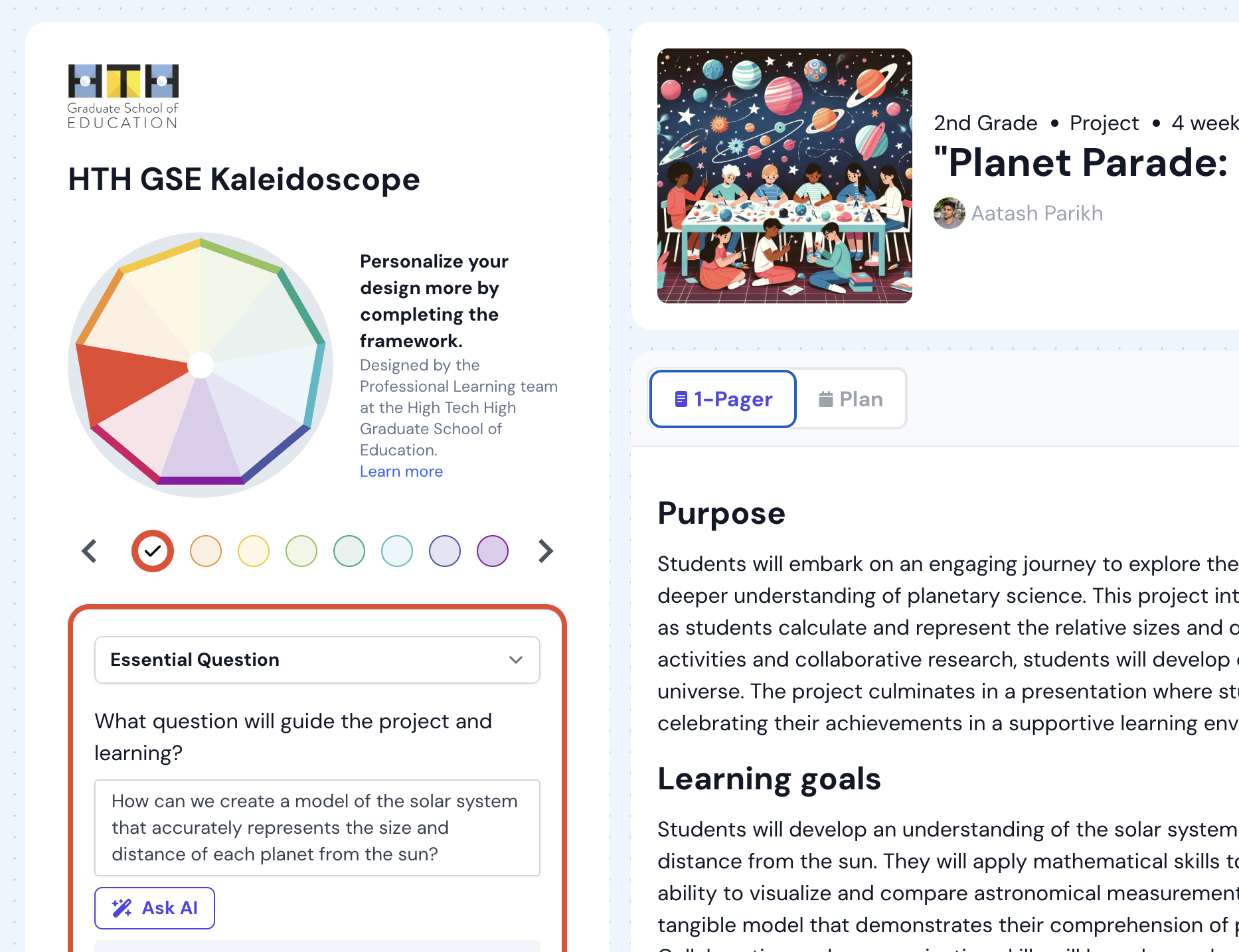
Inkwire's AI-assisted planning tool is always aligned to a high-quality instructional framework. Whether it's an open source framework from one of our partners or your own custom instructional framework, Inkwire helps align learning design to research-backed best practices.
Learn more about our partner frameworks from RevX by Transcend Education and the High Tech High Graduate School of Education.
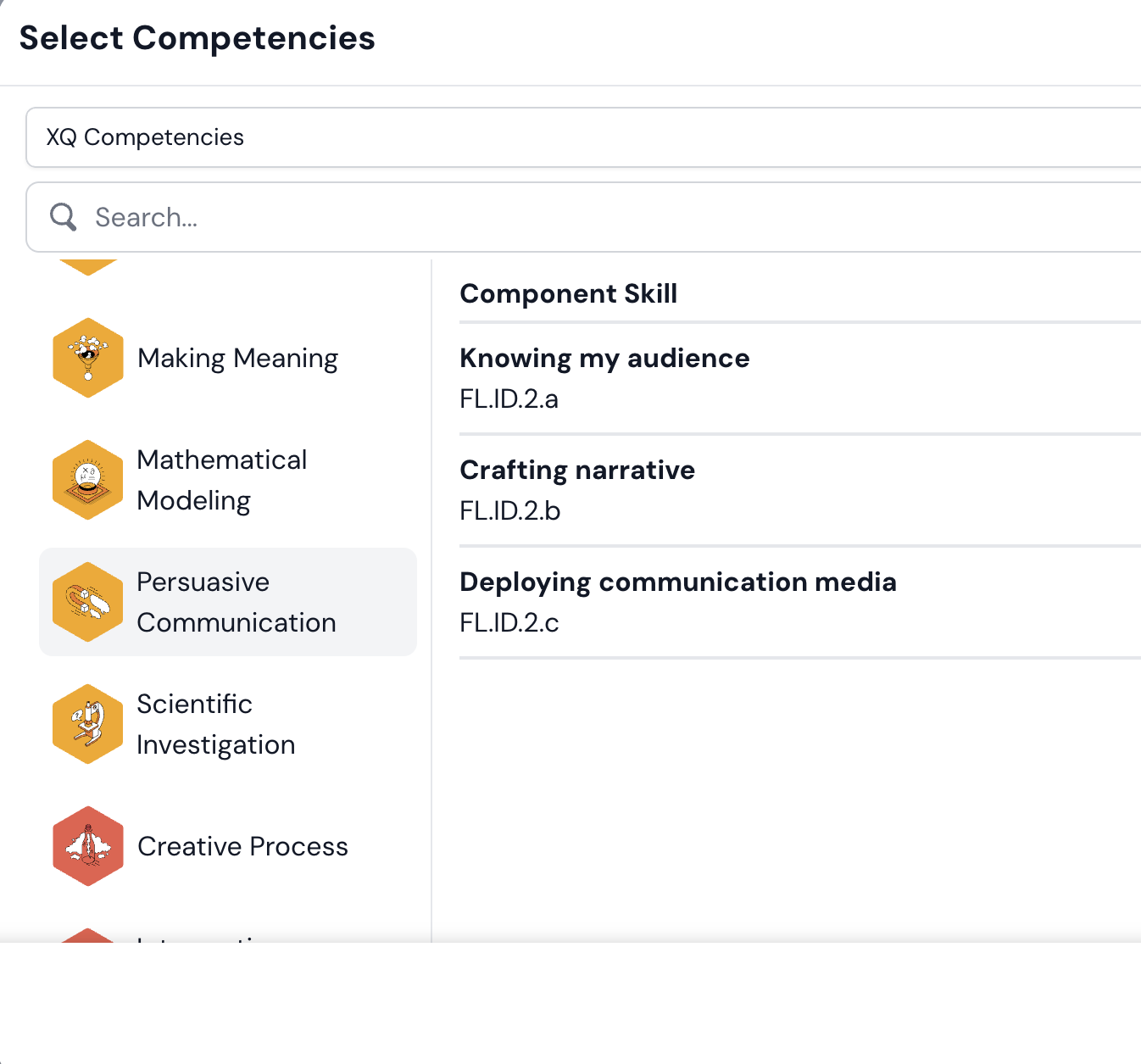
Integrate standards—and grad portrait competencies
Inkwire makes it easy to align units and lessons to national, state, or district academic standards. You can also import your local competency framework—such as your Portrait of a Graduate—so teachers can design learning experiences that build and assess the skills your community values most.
Inkwire also has built-in integrations with the Future9 Competencies and the XQ Competencies, giving educators trusted options for future-ready competencies.
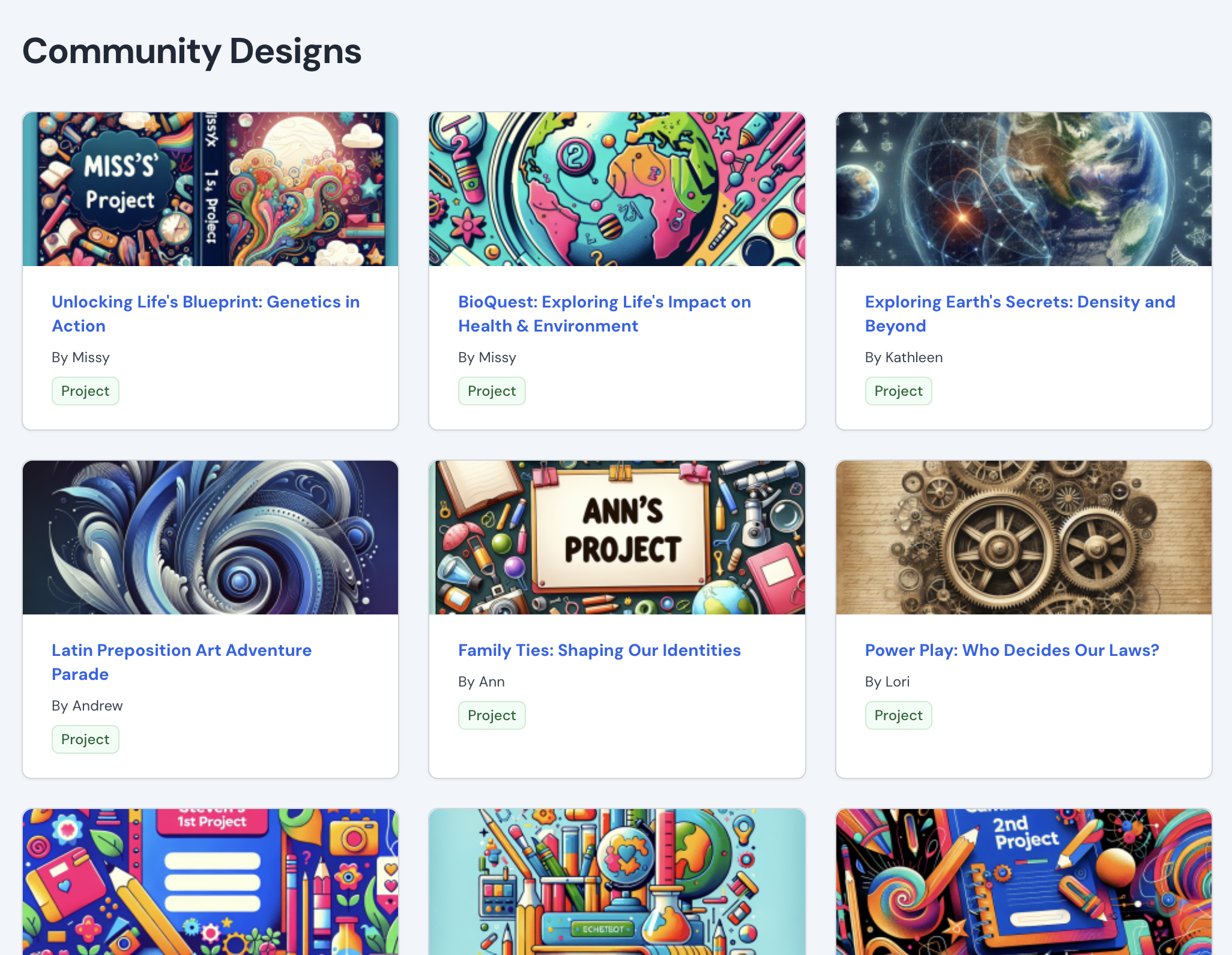
Develop and activate community assets
Inkwire helps foster collaboration in your organization by helping you build out an internal library of content and curriculum. You can also upload local instructional resources and make them available within the learning experiences designed by your community.
Build a database of local partners—from community members to industry experts—for educators & students to integrate into the design of a learning experience.

Build a future-ready portfolio system
Inkwire’s digital portfolio platform allows learners to capture and showcase their work in multiple formats—reflections, writing, photos, videos—all aligned to standards and competencies. As students tag and organize evidence, they build portfolios that demonstrate readiness for graduation, capstone defenses, or real-world opportunities.
Educators and district leaders can track growth over time and monitor mastery of skills aligned to your Portrait of a Graduate or local competency framework. Whether you’re supporting student-led defenses or system-wide performance assessments, Inkwire helps make learning visible and actionable.
Ready to learn more?
Connect with usWhat educators are saying...
“We are starting an adventure with PBL. This is going to help our team brainstorm and develop so many ideas!”
“This is the innovative, creative PBL work that I’ve been striving for … Every teacher needs to use this software. EVERY teacher.”
“Easy to use with standards available and allows me to discover other projects and refine to meet my needs.”
“This program made a world of difference in developing lessons with integrity.”
“Easy access to CTE and ELA standards; quickly offers ideas, provides pacing suggestions, and gives a solid starting point for outlining unit steps.”
“I was able to find and create a full design for my PBL project.”
“This is amazing—very helpful for outlining a PBL project and a huge time-saver for teachers.”
“Inkwire simplifies the project-planning process dramatically.”
“This saved me so much time! It’s easy to use and easily adaptable when you want to add something.”
“It’s new to me, but I liked it from the first try. It gave me everything I needed for creating a lesson plan—something that normally takes a lot of time on my own.”
“So far, I’ve been very impressed with the ease of use and the quality of the results it produces.”
“Absolutely invaluable for planning a project.”
“An amazing tool for teachers to structure their PBL.”
“Me ha resultado fácil trabajar y de una manera muy intuitiva.”
“Very intuitive, appealing to the eye, and a GREAT resource for auditing PBLs. Thank you!”
“Thanks for making such a great product—the software was easy to navigate and helped me generate multiple project ideas in minutes.”
“The AI suggestions for the parts of the project I was unsure about helped me steer the project in the direction I wanted.”
“Super-friendly interface and a huge time-saver!”
“The product is genuinely user-friendly and addresses a specific need.”
“Easy to sign up, easy to use, and I love how the AI helps generate ideas.”






